MEGHAN MILBRATH, MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION, 2018
LEARNING TO IDENTIFY A COMMON CAUSE OF WINTER DEATH IN NORTHERN CLIMATES
Beekeepers in northern climates continue to lose many colonies every winter. I originally wrote this article in 2016 after talking with many beekeepers who all experienced the same issue. Two years later, we continue to see many colonies that are lost in the same way. Many beekeepers think that winter-time losses are due to the cold weather. Bees, like lots of animals, can handle cold weather if they are healthy. This issue is that the bees are not healthy going into winter (even if they look like they are in autumn). In this article, I’ll describe the most common type of wintertime honey bee loss for small scale beekeepers in the North. The sad news is that these losses continue to be occurring at high rates. The good news is that beekeepers can
take actions to reduce the risk and to keep their bees in good health.
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE COMMON EARLY WINTER DEATH IN NORTHERN STATES:
1. The colony was big and looked healthy in the fall
2. A lot of honey is left in the top supers
3. The cluster is now small, maybe the size of a softball
4. Near or just below the cluster is a patch of spotty brood – some fully capped, and some with bees dying on emergence (heads facing out, tongues sticking out).
5. If you look closely in the cells around the brood, you will see white crystals stuck to the cell walls, looking like someone sprinkled coarse salt in the brood nest.
AND
6. You don’t have records showing that varroa was under control.
Sound familiar?
We see this classic set of symptoms over and over in the states with a period of winter stress. A big colony seems to just shrink down and disappear. Many people want to use the term colony collapse for this type of death, and while collapse is a good descriptor of what happens, this is not true colony collapse disorder.
This is death by varroa-associated viruses.
How does it happen?
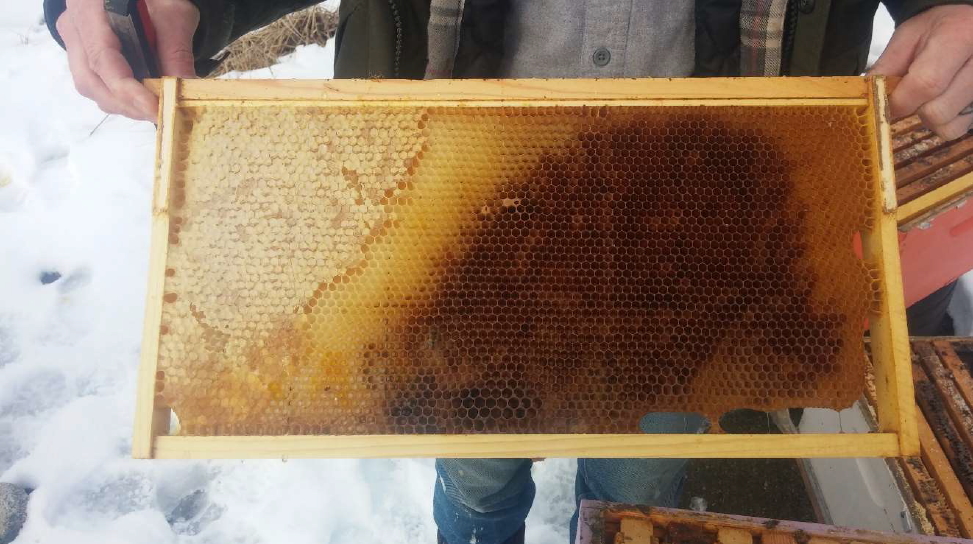
1. The big colonies –While beekeepers are often surprised that their big colonies are the ones that are gone first, it makes perfect sense in terms of varroa growth. Since varroa mites reproduce in capped brood, the colonies that make the most brood (i.e. got the biggest) are the ones most at risk of having a high population of varroa. Colonies that swarmed, or didn’t take off, or even fought a disease like chalk brood are less at risk from high varroa populations, because they didn’t consistently have large amounts of brood where varroa can reproduce. You should have good notes that say you had a large cluster going into winter, but even if you don’t, you can see the large circle of food eaten by a large cluster, indicating a high population of bees.
This colony had a large brood nest (indicated by the dark comb in this frame from the top deep box), and a large cluster going into winter (indicated by the large amount of honey that is eaten away where the winter cluster started). Varroa were never monitored or managed in this colony, and it was dead by February, if not sooner.

2. Lots of Honey – Lots of honey means that the colony died fairly early. Colonies with high levels of varroa tend to die fairly early in the season (before February), leaving lots of honey behind. Once the bees are stressed and in cluster, the viruses take their toll very quickly. In some cases the colony will even abscond in fall, or be dead before winter really hits.
The colony shown above had a third deep box that was filled with capped honey, indicating that the bees died early, and starvation was not the culprit.
3. Small cluster – Varroa levels peak right when the winter bees are forming. The bees that emerge from varroa infested cells are weakened, and more importantly, are riddled with viruses. Varroa mites are notorious for carrying deformed wing virus (DWV), but are known to transmit many more. In winter, the older summer bees die off, and there aren’t enough healthy winter bees that are strong enough to handle the stress of the cold. It is common to see some spotting (bee poop) near the dead cluster, leading many beekeepers to blame nosema. While Nosema apis can cause dysentery, it isn’t the only cause – it would be expected that a tiny, stressed cluster wouldn’t be able to properly take cleansing flights.
When a colony starves, the bees stick in the cells and drop to the bottom board, and you end up with a pile of dead bees in the hive. When bees get sick with viruses and other pathogens, however, they often will fly away. Sick bees by nature leave the colony to die in the field, an act designed to prevent pathogen transmission in the colony. When most bees are sick, they either fly away, or are too weak to return after cleansing flights. An early fall illness means that a lot of the bodies probably got removed by workers too. Sometimes, when the brood are too sick, the whole colony will abscond. Many people call these fall swarms, but often it is the colony leaving because the varroa/viruses are too bad.
In our colony, the cluster was only the size of our hand – some bees had their heads stuck in the cells, trying to stay warm, others had fallen between the frames
4. Patch of spotty brood / Bees dying on emergence – When a colony succumbs to varroa-associated viruses or parasitic mite syndrome (PMS), we see a lot of effects in the brood. Unlike American Foulbrood (AFB), which attacks the larvae at one particular stage, PMS will affect developing bees at many stages of development. It is one of the only diseases where you see bees dying right as they emerge.
Note the bee in the upper left is fully formed, and died on emergence. You can often see frozen/melted larvae along with dead pupae. Many beekeepers instantly suspect AFB, but AFB-infected colonies usually will not be large and would not have produced a lot of honey going into the winter.
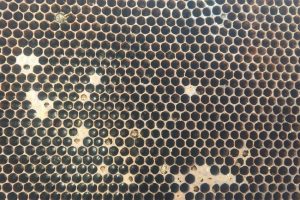
5. White crystals in the brood – Around the cells where the brood died (the last place of the brood nest), you will often see white crystals stuck to the walls of the cells. These are dry (not suspended in liquid like crystalized honey), and are the crystalized pee of varroa. Varroa mites defecate in the cells, and the resulting guanine crystals are left behind, and visible to the naked eye.
The open cell to the lower right of the drone brood contains small crystals of guanine acid, indicating varroa defecation. The mite frass is dry and stuck to the walls on the cells. Many dead hives will also contain crystalized honey, but it will appear wet/liquid appearance, and largely in the bottom of the cell.

6. No records that varroa was under control. Notice that this says ‘varroa was under control’, and not that ‘the colony was treated’. You may have applied a treatment, but it may have been too little, or (more likely) too late. 2015/2016 was a particularly difficult year for this, because Michigan, like many places had a really late summer – it stayed warm enough for beekeepers to go into their hives well into October. Many beekeepers took the extra time to put on a varroa
treatment, thinking that they were lucky to get one in. While that treatment could help the bees for next season (by giving it a clean start to the next year), it was too late for that winter because the winter bees were already damaged. September and October treatments would have been applied after varroa had gotten to their winter bees. Winter bees are born in the fall, and with their special fat deposits that allow them to live through the winter months, they are the one who carry the colony to the next season. If the winter bees have already been infected with viruses, the damage is done. No amount of treatment or varroa drop after winter bees are damaged can bring a colony back.
The only way to know that you have varroa under control is to monitor using a sugar roll or an alcohol wash. Just looking at the bees does not work; varroa mites are so sneaky, that you rarely ever see them, unless the infestation is out of control, and by then it is too late. Many beekeepers say that they never see varroa in their hives, so they don’t think that they have a problem. In fact, a varroa infested hive can actually look like it is thriving. Underneath the lovely brood cappings, and away from our view, the mites are reproducing and biting the developing bees. The colony can look fairly healthy until the mites reach a threshold, and the colony succumbs to disease. By the time you see parasitic mite syndrome, or see varroa crawling on bees, it is often too late for that colony (especially if winter is just around the corner). Getting on a schedule of monitoring and managing mites will give you peace of mind that your healthy looking colony is indeed healthy.
The silver lining
If the above scenario is familiar, don’t despair. First, you are not alone. Many beekeepers got caught off guard with varroa this year. They didn’t realize how bad it was, or got thrown off by odd weather patterns. Second, when the bees die, the varroa mites die too. We don’t yet have evidence that the viruses would stay in the equipment, so you can reuse your old frames. The honey that is left can be extracted to enjoy (if you didn’t feed or medicate), and frames of drawn comb can be given to new colonies. Most importantly, if you recognize the above scenario in your colonies, you now have more knowledge as to what is harming your bees, and you can take positive action. You have time for this season to develop a strategy. Monitor your varroa mite levels using a sugar roll kit, or alcohol wash, read about integrated pest management for varroa, and make a commitment to prevent high mite levels this year before your winter bees are developing.
This is going to be the year!
Meghan Milbrath, Ph.D., MPH
mpi@msu.edu / www.pollinators.msu.edu / 517-884-9518

